Find the minimum number of ‘move-to-back’ required to sort an array
Python based approach
Problem
You are given an array of integers. Return the minimum number of ‘move-to-back’ required to sort the array in ascending order.
A ‘move-to-back’ is defined as removing an integer from it’s current position and pushing it to the end of the array

Sample Input: [1,4,2,5,3] | Expected Output: 2
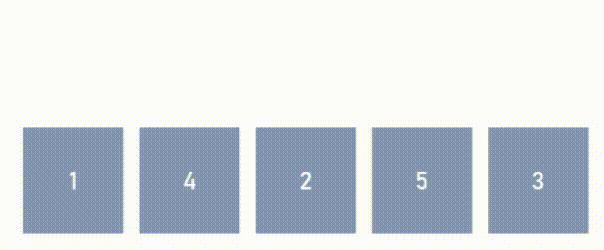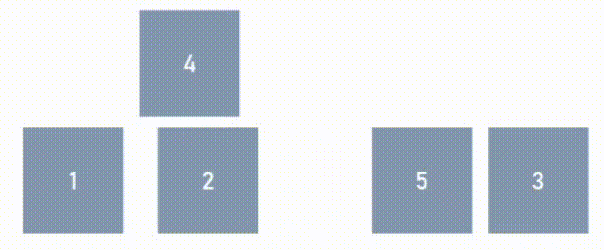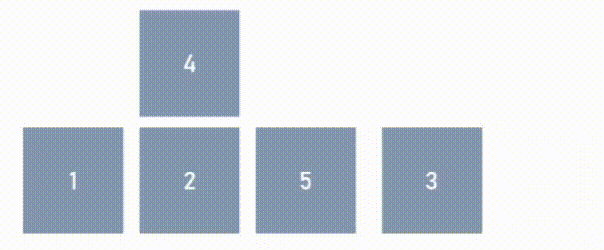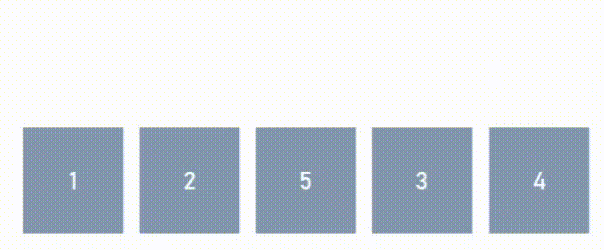

The solution to this problem is not immediately obvious. Although it might be tempting to take the approach of identifying the order in which elements need to be moved, it is important to note that the question is asking for the # of minimum of moves to complete this task, and not for the moves itself.
Approach
Find the number of elements in the correct relative position in relation to the sorted array.

Observation
- 1st, 3rd and 5th elements are already in relative sorted position.
- 2nd and 4th elements are not in relative sorted order.
From the figure above, N = 3. The number of ‘move-to-back’ can now be calculated by subtracting N from the total length of the array. Here, we are ignoring the values of the elements which need to be moved, instead we are only interested in the number of elements which need to be moved.
# ‘moves-to-back’ = len(arr)-N = 5-3 = 2
Code
Once the approach has been understood, the implementation of the code is relatively straightforward.
def countMoveToBack(input): # input array
# sort given array
sorted_array = sorted(input)
sorted_idx = 0
# initialize counter
# loop through given array
for i in range(len(input)):
if input[i] == sorted_array[sorted_idx]:
sorted_idx += 1
min_moves = len(input) - sorted_idx
return min_movesTime Complexity — O(nlog(n))
Space Complexity — O(n)
- where n is the size of the input array
Variations
- Calculate number of ‘move-to-front’
- Sort in descending order
If you’ve found this walkthrough useful, would greatly appreciate a tasty clap. Let me know if you’ve found better solutions to this problem.
